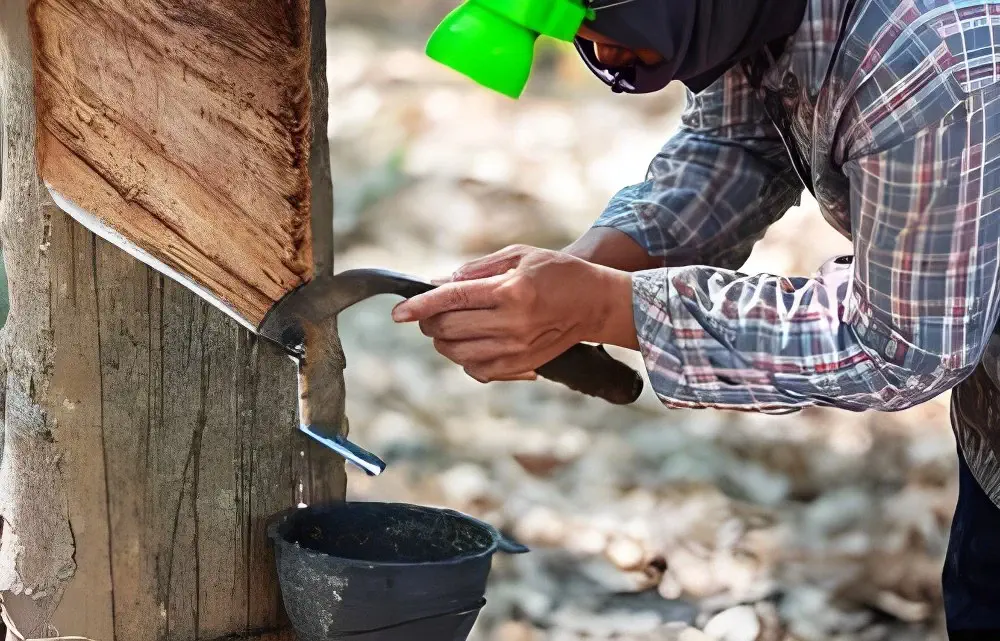
Thailand's Rubber Exports Face Extended Decline Amid Global Headwinds
Thailand's rubber industry continues to struggle with declining export performance, experiencing a 38% drop in export value from February to May 2025. Major markets including China, the United States, Japan, and Germany have significantly reduced their purchases, creating substantial challenges for Thai exporters navigating volatile pricing, weakening global demand, and ongoing trade uncertainties.
Export Performance Shows Persistent Weakness
Thailand's rubber export sector has experienced a sustained downturn since reaching its 2025 peak in February. Export values declined from $598.19 million in February to $377.94 million by May, representing a substantial erosion in revenue over just three months. This downward trajectory reflects broader challenges facing the global rubber market.
The volume decline mirrors the value drop, with shipments falling from 290,092 tons in February to 192,957 tons in May. This consistent month-over-month deterioration signals fundamental shifts in global demand patterns rather than temporary market fluctuations.
China's Dramatic Import Reduction Drives Market Decline
China's role as Thailand's primary rubber customer makes its import reductions particularly significant for the market. Chinese purchases plummeted by over 60% in value terms from February to May, with import volumes collapsing from 144,658 tons in February to just 57,107 tons in May.
This dramatic reduction stems from multiple factors affecting China's tire manufacturing sector, including ongoing concerns about potential trade policy changes under the Trump administration and China's broader economic recovery challenges. The consistency of China's month-over-month import reductions suggests structural rather than cyclical factors are at play.
Mixed Signals from Other Major Markets
United States Market Volatility
The U.S. market demonstrated significant volatility throughout the period. After an initial surge from $37.52 million in February to $50.24 million in March, American imports declined sharply to $34 million by May. While import volumes remained relatively stable, the declining values indicate downward pricing pressure and possible shifts in product specifications.
Japan's Inconsistent Demand Pattern
Japanese rubber imports followed an erratic pattern, declining from February to March, recovering in April, then falling again in May. This inconsistency likely reflects uncertainty in Japan's automotive sector regarding supply chain strategies and potential trade policy impacts.
European Market Challenges
Germany's rubber imports showed the most consistent decline pattern among major markets, falling steadily from $10.39 million in February to $7.52 million in May. This reflects broader challenges facing European automotive manufacturers, including elevated energy costs and economic pressures affecting the industrial sector.
Price Dynamics Reflect Supply-Demand Imbalances
STR20 rubber prices experienced significant volatility throughout May, highlighting the market's sensitivity to both supply constraints and competitive pressures. Prices climbed from $1,785 per metric ton on May 2 to a monthly peak of $1,885 per metric ton on May 14, driven by supply tightening measures and weather-related production delays.
However, this rally proved unsustainable as alternative suppliers from Africa and Vietnam increased their market presence. By month-end, prices had collapsed to $1,760 per metric ton, demonstrating the market's vulnerability to supply substitution from competing origins.
The Thai government's intervention through the Rubber Authority of Thailand (RAOT), which encouraged farmers to suspend tapping operations during low-price periods, provided temporary price support but failed to address underlying demand weakness.
Supply Chain Disruptions Add Complexity
A fire incident at North East Rubber Public Company Limited's warehouse in July affected approximately 10,000-15,000 tons of finished rubber products. While production facilities remained operational and no significant shipping delays occurred, such incidents highlight the vulnerability of concentrated production and storage facilities to operational disruptions.
Market Outlook Considerations
The sustained decline in Thailand's rubber exports reflects multiple converging challenges: shifting global automotive demand, intensified competition from alternative suppliers, trade policy uncertainties, and structural changes in key importing markets. The consistency of the decline across multiple major markets suggests these are not temporary disruptions but rather fundamental shifts requiring strategic adaptation by Thai exporters.
The volatility in pricing and the success of competing suppliers in capturing market share during Thailand's supply constraints indicate that market leadership positions can shift rapidly in response to availability and pricing dynamics. Thai exporters may need to reassess their competitive positioning and supply chain strategies to address these evolving market conditions.
This analysis draws from research and insights provided by Helix Tap. For more market intelligence and analysis, visit helixtap.com